Nautilus Design
Overview
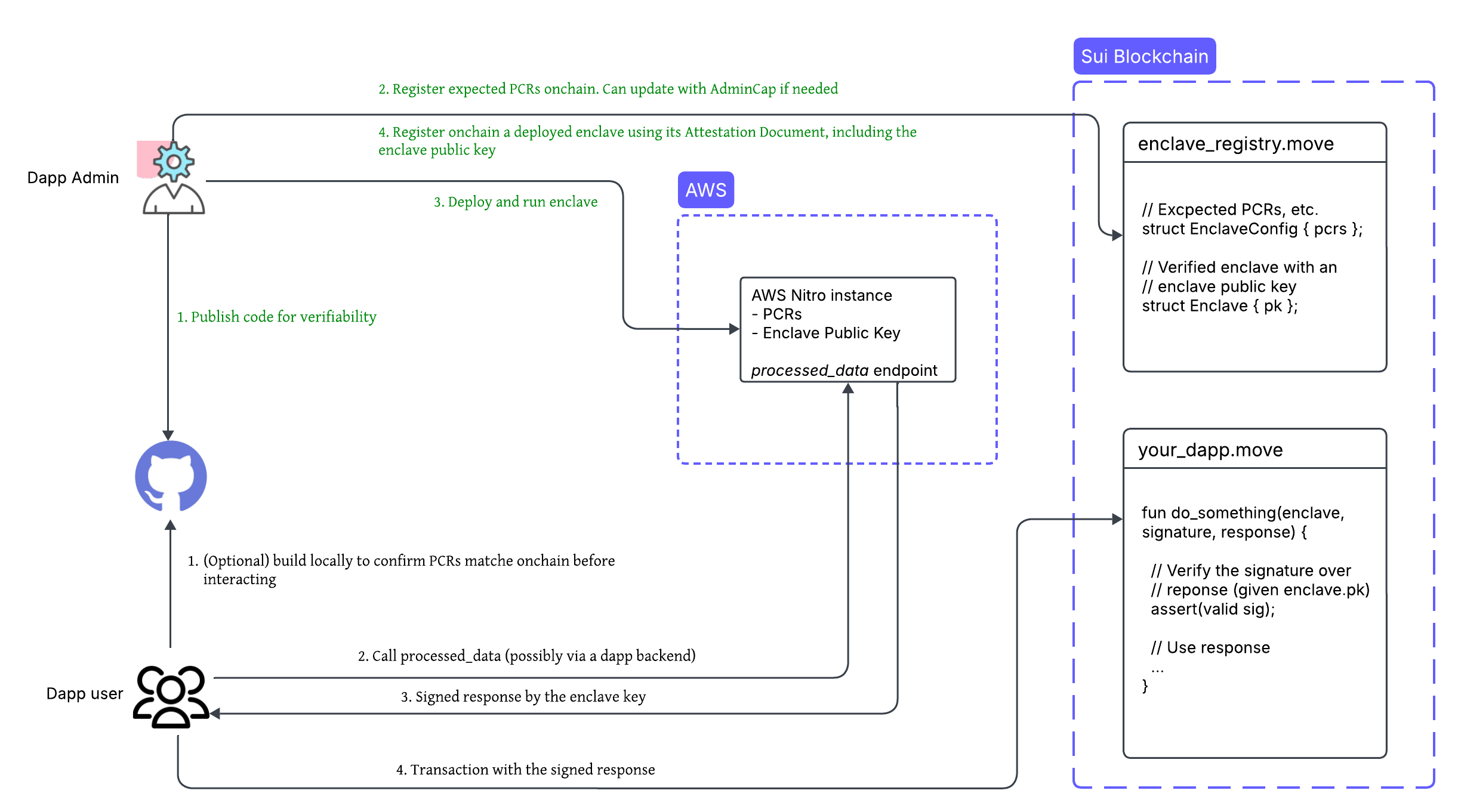
Dapp developer actions
- Create a Nautilus offchain server with a reproducible build. You may or may not start from the provided template.
- Publish the server code to a public repository (such as GitHub) to ensure transparency and verifiability.
- Register the instance’s Platform Configuration Registers (PCRs) using a Sui smart contract.
- Deploy the server to an AWS Nitro Enclave.
- Register the deployed enclave using a Sui smart contract and the attestation document. This step also includes registering the enclave’s public key, which is an ephemeral key securely generated within the enclave, and used for signing the enclave responses.
It’s recommended to route access to the enclave through backend services that handle load balancing, rate limiting, and other related aspects, to reduce the trusted computing base.
Verifying an attestation document onchain is a relatively expensive operation and should be performed only during enclave registration. After registration, use the enclave key to verify messages from the enclave more efficiently.
Dapp user / client actions
- (Optional) Verify the Nautilus offchain server code by building it locally and confirming that the generated PCRs match the onchain records.
- Send a request to the deployed enclave and receive a signed response.
- Submit the signed response onchain for verification before executing the corresponding application logic.
Trust model
The attestation document from an AWS Nitro Enclave includes a certificate chain that can be verified onchain using AWS as the root certificate authority. This verification confirms the following:
- The enclave instance is running unmodified software, as validated by its Platform Configuration Register (PCR) values.
- Users can independently verify that the instance’s computation aligns with the published source code, ensuring transparency and trust.
Reproducible builds allow developers and users to optionally verify that the binary running inside an enclave instance matches a specific version of the source code. This approach provides the following benefits:
- Anyone can build and compare the binary to confirm consistency with the published source code.
- Any changes to the software result in different PCR values, making unauthorized modifications detectable.
- Reproducible builds shift the trust from runtime to build time, strengthening the Dapp’s overall security posture.
Reproducible builds may not apply to all use cases, such as when the source code cannot be made public.